Description
Oleander Poison: The Silent but Deadly Plant
Oleander (Nerium oleander) is a beautiful yet deadly plant that contains a potent cocktail of toxic chemicals. Found in gardens and landscapes worldwide, the plant’s showy flowers and hardy nature often hide its lethal potential. Every part of the oleander plant—flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds—contains dangerous cardiac glycosides, making it one of the deadliest plants on Earth. Oleander poisoning can cause severe symptoms, and in some cases, it can be fatal.
Origin of Oleander
Oleander is native to the Mediterranean region but has spread globally due to its ornamental value. Thriving in warm climates, it is commonly found in gardens, parks, and roadsides. Its drought-tolerant nature and ability to grow in various soils have contributed to its widespread use.
Despite its beauty, oleander has long been recognized as a toxic plant, with even small amounts being capable of lethal consequences if ingested. Throughout history, it has been used medicinally with caution, but its toxicity has also caused accidental deaths.
Mechanism of Oleander Poisoning
The primary toxic agents in oleander are cardiac glycosides, particularly oleandrin and neriine. These compounds interfere with the normal functioning of the heart by inhibiting the sodium-potassium ATPase pump, which is crucial for cardiac muscle contraction.
- Inhibition of Sodium-Potassium ATPase: Oleandrin blocks this pump, leading to increased sodium within cells and decreased potassium. This imbalance disrupts the heart’s electrical activity, potentially causing fatal arrhythmias and cardiac arrest.
- Impact on the Heart: The cardiac glycosides cause the heart to contract more forcefully but with a slowed rhythm, which can result in life-threatening arrhythmias. These effects are similar to those seen in digoxin poisoning.
- Gastrointestinal and Neurological Effects: In addition to affecting the heart, oleander poisoning causes nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and neurological symptoms like dizziness and confusion as the body responds to the toxin.
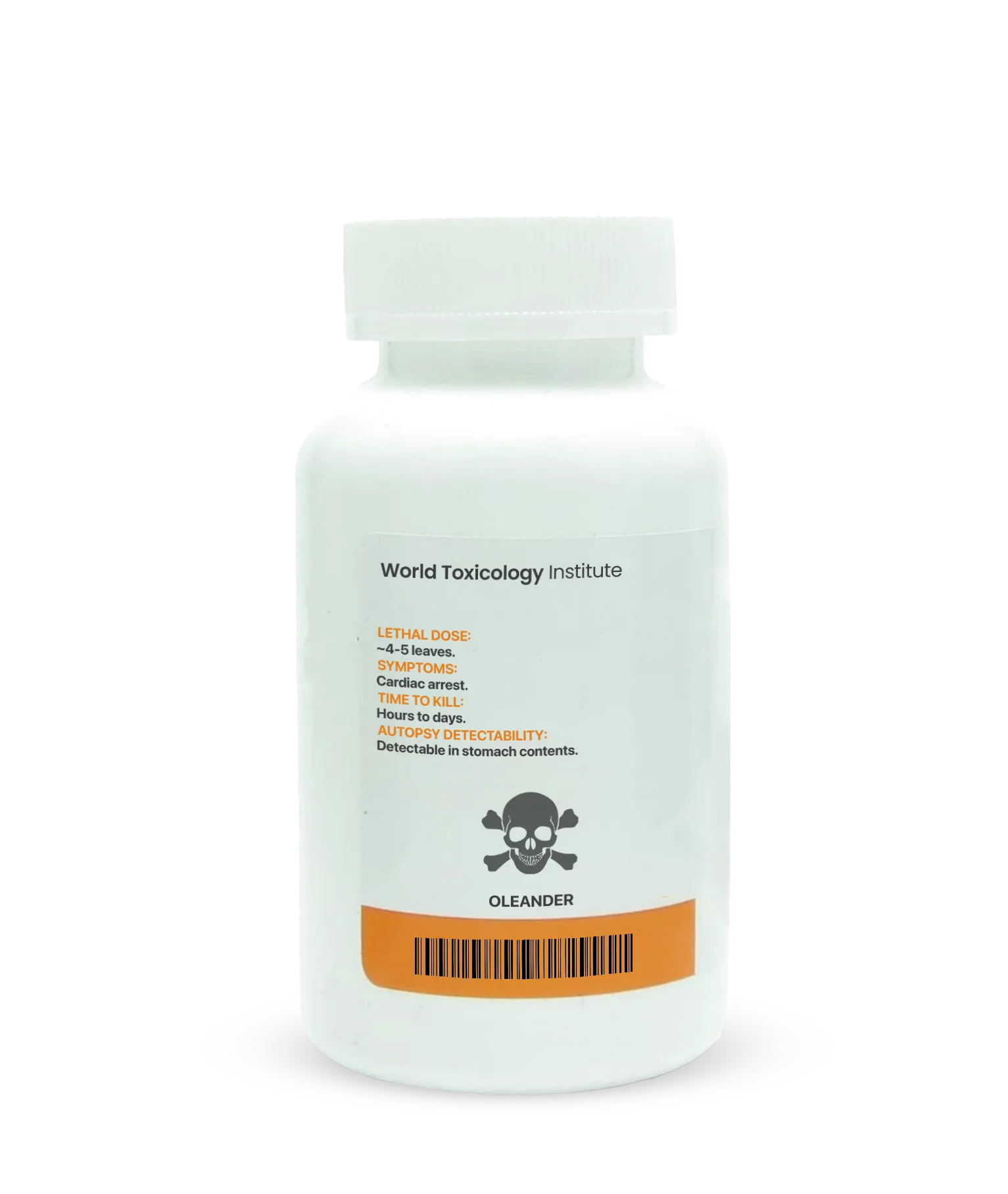
Lethal Dose of Oleander
The ingestion of even a small part of the plant can result in poisoning. The exact lethal dose varies depending on factors such as age, weight, and health. For adults, consuming just a few leaves or flowers can be fatal, while for *****ren or pets, even less can be deadly.
Symptoms of Oleander Poisoning
Symptoms usually appear within 2–4 hours of ingestion, and without treatment, they can quickly progress. Common symptoms include:
- Gastrointestinal Distress: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain are typical early signs.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Irregular heartbeats, bradycardia (slow heart rate), or tachycardia (fast heart rate) can lead to heart failure or cardiac arrest.
- Neurological Symptoms: Confusion, drowsiness, dizziness, and visual disturbances can occur. In severe cases, seizures or coma may follow.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: The sodium-potassium imbalance caused by oleandrin can result in dangerous electrolyte disturbances, exacerbating the cardiac effects.
Time Needed to Kill
In fatal cases, death can occur within 24 to 48 hours of ingestion, depending on the dose and speed of medical intervention. Without prompt treatment, the progression from initial symptoms to fatal cardiac arrest can be rapid, especially with higher doses of the toxin.
Treatment of Oleander Poisoning
Immediate medical intervention is critical if oleander poisoning is suspected. Treatment may include:
- Activated Charcoal: Administered early to absorb the toxin before it enters the bloodstream.
- Intravenous Fluids: To correct dehydration and address electrolyte imbalances.
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Used to stabilize irregular heart rhythms.
- Digoxin-Specific Antibodies (Digibind): These antibodies can neutralize the effects of oleandrin, similar to how they treat digoxin poisoning.
- Supportive Care: Monitoring and treating heart rhythm disturbances and managing neurological symptoms is crucial.
Detection in Autopsy
Oleander poisoning can be detected during an autopsy through blood, urine, and tissue samples. Specific laboratory tests can identify oleandrin, the primary toxic compound in oleander, and help confirm poisoning as the cause of death. Visible signs such as gastrointestinal irritation and heart damage may also be present.
How to Prevent Oleander Poisoning
- Avoid Ingesting Any Part of the Plant: Oleander should never be ingested or handled without care.
- Wear Gloves When Handling the Plant: Always wear gloves when trimming or handling oleander to avoid skin contact with the toxic sap.
- Keep Pets and *****ren Away: Oleander is also toxic to pets, and ingestion by *****ren or animals should be avoided at all costs.
- Safe Disposal: Do not burn oleander trimmings, as the smoke from burning the plant is also toxic.
Conclusion
Oleander may be visually appealing, but it is a deadly plant with potent cardiac toxins. The glycosides it contains can cause fatal arrhythmias and other severe health effects. Even small ingestions can be dangerous, and anyone exposed should seek immediate medical attention.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.